How AI is fast-tracking biotech breakthroughs
August 08, 2025
Whenever we mention uses of AI, the thoughts of AI chatbots, image generators, and AI in social media algorithms come to mind. These are the visible uses of AI in our day-to-day lives.
However, in hindsight, AI has had a tremendous impact on many other sectors. One such lesser-discussed sector is biotechnology.
There are groundbreaking advancements in drug discovery, genomics, personalized medicine, and other areas of research and development. AI has the potential to revolutionize healthcare.
How AI can change the biotech scene
On one hand, AI is predicting and detecting diseases faster and with more accuracy. On the other hand, it is accelerating ongoing research and developments in healthcare. AI is enhancing the precision and efficacy of medical intervention.
Drug development is a time-consuming process, not to mention what a costly endeavor it is. It often takes more than a decade and billions of dollars to test and bring a new drug to the market.
Even years of trial-and-error process can go in vain. And, there is always a chance of discovering new side effects.
Today, however, with the aid of AI, we can design novel molecules and predict their interactions with biological targets.
Antiverse is one such biotech startup that designs antibodies with the help of AI, significantly speeding up the drug development process.
With the help of AI models, we can predict the impacts of drugs earlier in the development process. In the process, scientists are improving efficiency and also the safety in later-stage development.
A global management consulting firm, McKenzie and Company, frequently analyzes industry trends, market potential, and the economic impact of emerging technologies.
They have estimated that generative AI could create $60-100 billion annually in value for pharmaceutical companies.
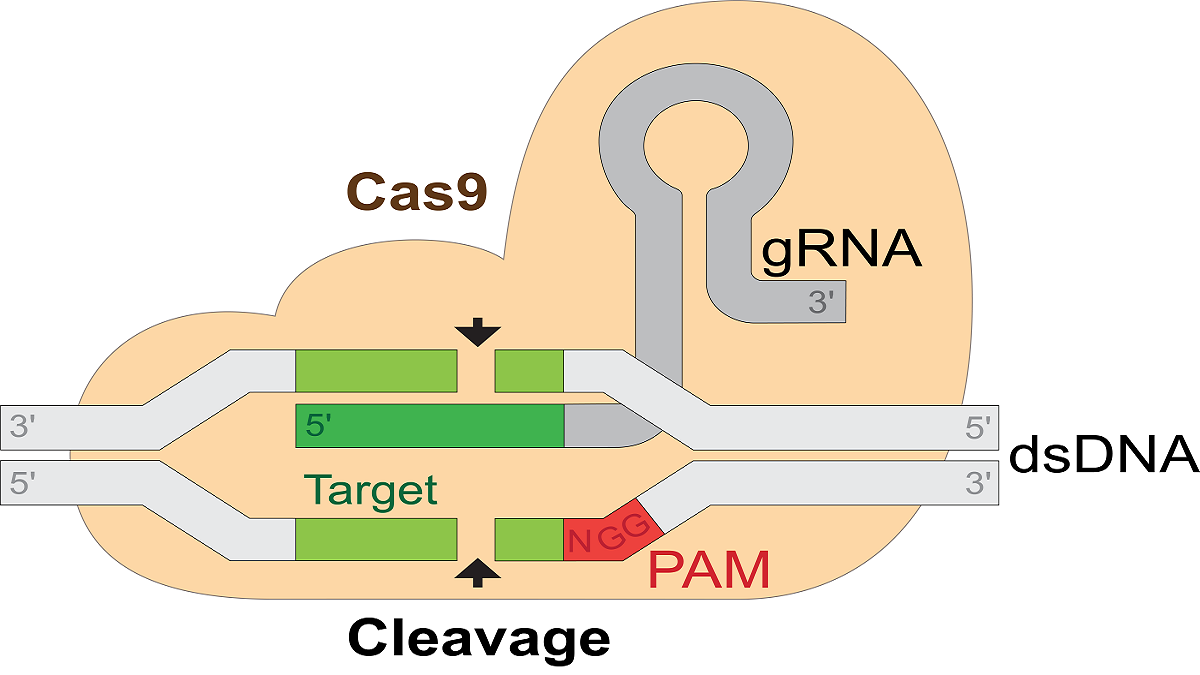
How is it done?
The combination of AI and Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, i.e, CRISPR gene editing technology, has significant impacts in medicine and climate change. Scientists edit genes by cutting DNA at specific locations, using a tool called CRISPR-Cas9.
However, unintended off-target or accidental mutations sometimes occur. AI predicts where CRISPR might make unintended cuts and suggests more accurate methods for editing genes.
AI handles vast genomic data sets. AI scans genetic databases to identify genes associated with disease and suggests where CRISPR could be utilized for therapeutic purposes.
As mentioned earlier, traditional CRISPR relies on trial-and-error methods; however, AI accelerates this process by simulating millions of edits before conducting real-world experiments. As a result, researchers can make discoveries more efficiently.
In public databases, AI has been implemented to identify Gene editing proteins and then to predict heat-tolerant RNA molecules.
These molecules have practical applications in improving biomanufacturing processes and developing more effective therapies for genetic diseases.
AI has paved a whole new path for personalized medicine. AI processes the patient’s genetic data to identify mutations or genes associated with them. Then, the prediction is made of which drug might work best on that unique genetic makeup.
First, analyzing patient data, then predicting treatment outcomes, and finally recommending personalized drug dosages, AI can assist throughout the process.
One example of this is cancer treatment. AI identifies specific gene mutations in a patient’s tumor and then selects a targeted drug.
Millions of patient records are fed into AI models to see how people with similar genetic profiles respond to drugs. Then, the best dosage and combination of medications for a particular individual is calculated.
A detailed computer model of organs, cells, or even the entire body is made, which is called digital twinning. To make a digital twin of a person, medical records, genetic information, real-time health data, and lifestyle factors are used.
AI processes this data to simulate how a person’s body would react to different diseases, treatments, or medications.
Before administering a new drug to a patient, it is first tested on their digital twin, allowing for the prediction of effectiveness and potential side effects. We can avoid potential medical side effects or other implications by analyzing these simulations.
For example, digital twins of cancer patients can be used to predict their response to chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
Personalized surgery simulations, simulating disease progression, creating virtual organs for transplant research, etc., are also done using digital twinning.
Currently, scientists are developing virtual models of human cells using generative AI. The target is to simulate cells and predict the effects of drugs, mutations, and viruses.
Major AI breakthroughs in biotechnology
Lambique Therapeutics, backed by Nvidia, recently built an AI model that can design molecules and predict their effectiveness. This model reduces drug development time from years to months.
The decades-old protein-folding problem has been solved by an AI model called AlphaFold. Google’s DeepMind developed the AlphaFold AI model. AI-driven image processing and visualization are game changers in the biotechnology field.
Google’s Med-PaLM and Path-AI are two models that are improving the accuracy of X-rays, CT scans, and pathology slides. Similar models are used in detecting cancer and tumors faster than human radiologists. And we have already mentioned the CRISPR Gene editing technology.
All these AI technologies and models require massive amounts of patient data to predict results. A vast amount of data sets are fed into these models.
While the integration of AI in biotech has revolutionized various sectors, medical data is particularly sensitive due to the private and confidential nature of patient information.
Hence, a clear regulatory framework concerning data bias and transparency of air algorithms is imperative. It is vital that data privacy is ensured and sensitive genetic information is handled securely.
There is no denying that the fusion of AI and biotechnology marks the beginning of a new era of medical and scientific breakthroughs. Responsible use of this technology must be ensured.
Most Read
Electronic Health Records: Journey towards health 2.0

Making an investment-friendly Bangladesh

Understanding the model for success for economic zones

Bangladesh facing a strategic test

Bangladesh’s case for metallurgical expansion

How a quiet sector moves nations

A raw material heaven missing the export train

Automation can transform Bangladesh’s health sector

A call for a new age of AI and computing
You May Also Like
